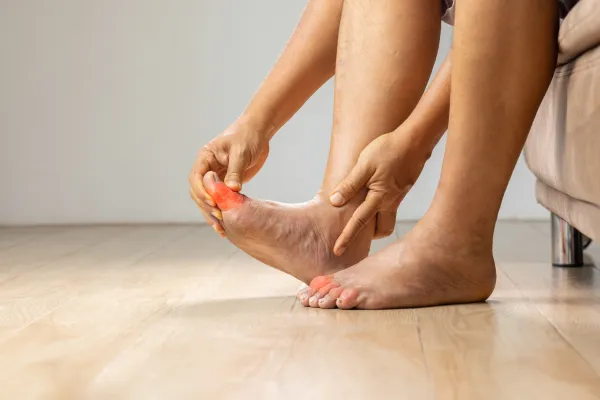
Ankle Arthritis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
If you’ve been experiencing persistent ankle pain, stiffness, or swelling, you might be dealing with ankle arthritis. This condition can significantly affect your mobility and quality of life, but with the right care and treatment, it’s possible to manage the symptoms and regain your comfort. In this blog post, we’ll explore how arthritis affects the ankle, the symptoms to watch out for, and the treatment options available to help you get back on your feet.
What is Ankle Arthritis?
Ankle arthritis occurs when the cartilage that covers the bones in the ankle joint begins to wear down, causing the bones to rub against each other. This breakdown can lead to pain, inflammation, stiffness, and decreased mobility. There are several types of arthritis that can affect the ankle, including:
Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most common type of arthritis and typically develops with age. It occurs when the cartilage in the joint breaks down over time due to wear and tear.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune condition that causes the body’s immune system to attack healthy joints, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis develops after an injury, such as a sprain, fracture, or dislocation, which can lead to long-term damage to the joint.
Gout: A form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint, leading to sudden and severe pain.
Symptoms of Ankle Arthritis
The symptoms of ankle arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but common signs include:
Pain: A dull or sharp pain in the ankle joint, which may worsen with activity or after periods of rest.
Stiffness: Difficulty moving the ankle or limited range of motion, especially in the morning or after sitting for a long period.
Swelling: Inflammation around the ankle joint, which may make the joint appear puffy or feel tender to the touch.
Decreased Mobility: Difficulty walking or standing for long periods, and a feeling of instability when bearing weight on the ankle.
Crunching or Grinding Sensation: A feeling or sound of bones rubbing together when moving the ankle due to the loss of cartilage.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to get a proper diagnosis to determine the type of arthritis affecting your ankle.
Diagnosing Ankle Arthritis
To diagnose ankle arthritis, your podiatrist will begin with a thorough physical examination, asking about your symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries to the ankle. Diagnostic tests may include:
X-Rays: X-rays can show the degree of joint damage and help identify the loss of cartilage, bone spurs, or other signs of arthritis.
MRI: An MRI provides a more detailed image of the soft tissues, including cartilage, ligaments, and tendons, and can help identify the severity of the damage.
Blood Tests: If rheumatoid arthritis or gout is suspected, blood tests may be used to detect markers of inflammation or uric acid levels.
Treatment Options for Ankle Arthritis
While ankle arthritis can’t be fully cured, there are several effective treatment options to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the arthritis and the specific needs of the patient.
1. Conservative Treatments
For mild to moderate cases of ankle arthritis, conservative treatments can be very effective in reducing pain and improving mobility:
Rest and Activity Modification: Taking breaks from high-impact activities like running or jumping can give your ankle time to heal and prevent further damage.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice to reduce swelling or heat to relax stiff muscles and joints can provide immediate relief.
Over-the-Counter Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation. Acetaminophen can also be used for pain relief.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can help you improve ankle strength, flexibility, and range of motion through targeted exercises, which can reduce pain and enhance mobility.
2. Footwear and Orthotics
Wearing the right shoes is crucial for managing ankle arthritis. Shoes with cushioning, arch support, and stability can reduce stress on the joint. Custom orthotics can also provide added support and correct foot mechanics, which helps alleviate pressure on the ankle joint and prevent further deterioration.
3. Injections
For more severe cases of ankle arthritis, injections may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation:
Corticosteroid Injections: These injections provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation and swelling in the ankle joint.
Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Hyaluronic acid can help lubricate the joint, reducing friction and improving mobility.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: PRP therapy uses a patient’s own blood to promote healing by injecting concentrated platelets into the affected area.
4. Surgical Treatments
If conservative treatments don’t provide relief, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options include:
Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where a small camera is used to inspect and clean the joint, remove damaged tissue, or repair cartilage.
Ankle Fusion (Arthrodesis): In cases of severe arthritis, ankle fusion may be recommended. This procedure involves fusing the bones of the ankle joint together to eliminate pain. However, this can limit the range of motion.
Ankle Replacement (Arthroplasty): Ankle replacement surgery involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one, which can help restore function and reduce pain, though it is typically reserved for older patients or those with advanced arthritis.
Preventing Further Damage
While some risk factors for arthritis, like age and genetics, cannot be controlled, there are ways to reduce the risk of further damage:
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the joints.
Wear proper footwear that offers support and cushioning.
Avoid high-impact activities that can exacerbate arthritis symptoms.
Stay active with low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to strengthen the muscles around the ankle joint.
Conclusion
Ankle arthritis can cause significant pain and limit mobility, but with early intervention and the right treatment approach, you can manage symptoms and maintain an active lifestyle. Whether through conservative measures or surgical options, there are many ways to address ankle arthritis and improve quality of life.
If you’re experiencing ankle pain or stiffness and think you may have arthritis, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Pomona Valley Podiatry Group. Our team is dedicated to providing personalized care and treatment options to help you stay active and pain-free.
Ask And His Team
Fill in the form to request a Call From Our Team
One of our team will call you for FREE and answer any questions or concerns you may have about your uncomfortable foot condition